The Normal Heart Rhythm
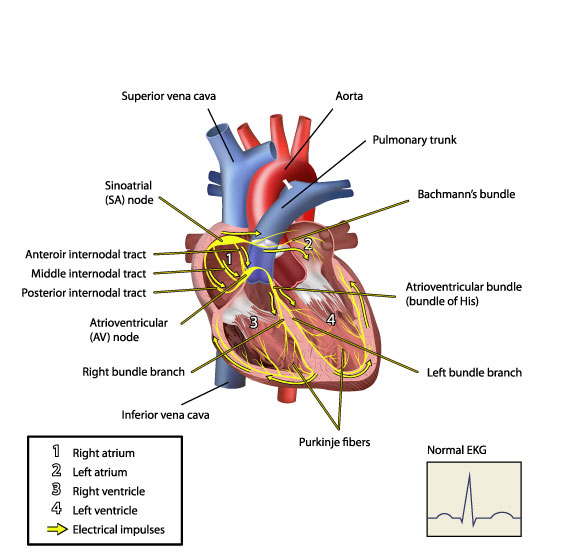
The human heart has four pumping chambers that circulate oxygen and nutrients through the body. The two top chambers, the right atrium and left atrium serve as primer pumps for the two bottom chambers, the right and left ventricles. The right and left ventricles pump the blood through the lungs and the entire body. The normal heart rhythm serves to activate and coordinate the pumping systems of the heart for optimal function. Each person’s heart rate depends on their level of activity, their athletic conditioning and their metabolic state. The heart rate while awake, at rest, may range between 50 to 100 beats a minute.
The normal heart rhythm is usually referred to as normal sinus rhythm. In the normal sinus rhythm, the cardiac impulse starts from the sinus node, the body’s natural pacemaker, located in the right atrium. The cardiac impulse activates the heart muscle cells in the right atrium and left atrium. The cardiac impulse is then transmitted to the left and right ventricles, through a special connecting structure called the atrioventricular node (AV node). The AV node delays the cardiac electrical impulse for a short period of time to allow the right and left atria to finish their pumping function into the right and left ventricles. The AV node then transmits the cardiac electrical impulse to the right and left ventricles through specialized conducting structures called the bundle of His, and the right and left bundle branches. The heart muscle in the right and left ventricle is activated by the cardiac electrical impulse to pump blood through the lungs and the entire body.
Click here to learn about abnormal heart rhythms.