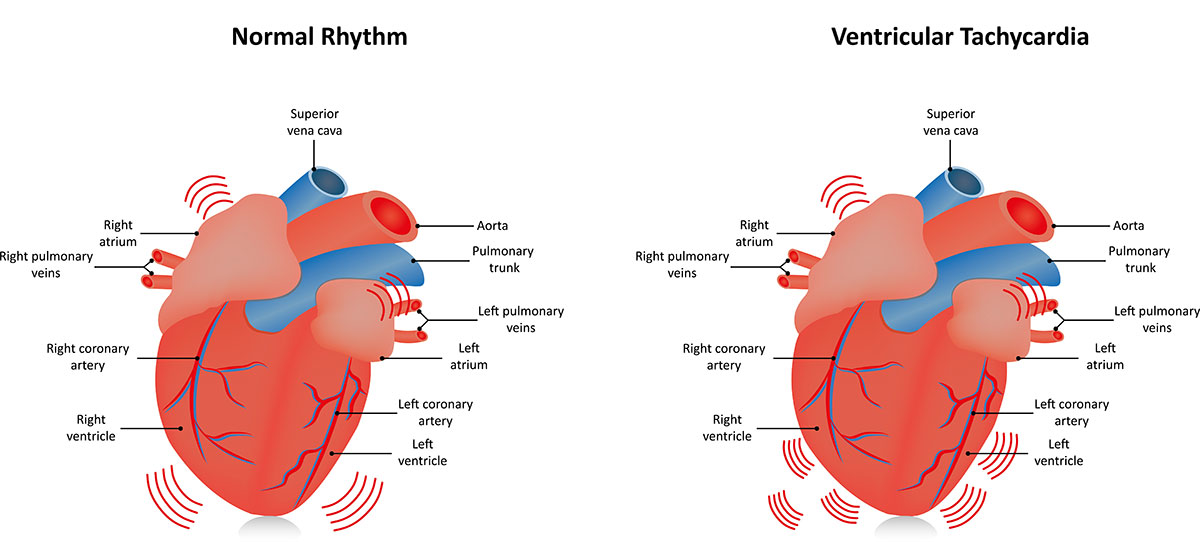
What is Ventricular Tachycardia?
Ventricular tachycardia is also called VT or V-tach (pronounced V-tack). Ventricular tachycardia occurs when abnormal cardiac impulses start in the heart ventricles (the two bottom chambers of the heart) and cause the heart to beat faster than normal. V-tach may start from heart muscle that has been damaged by prior heart disease, but it may also arise in a structurally normal heart. Ventricular tachycardia may be a particularly serious condition when it arises from heart muscle that is weakened from previous heart attacks or coronary blockages. In certain individuals, ventricular tachycardia may lead to cardiac arrest and sudden death.
Symptoms of Ventricular Tachycardia
The symptoms of V-tach depend on how long it lasts, how fast the heart is beating, and how healthy the heart is. The symptoms may include palpitations, racing heart feelings, rapid pulse, light headedness, fainting, chest pain, chest pressure, chest discomfort, anxiety or shortness of breath. In general, longer episodes and faster episodes tend to lead to more severe symptoms.